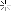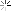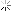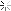Urning speed and feed rate are crucial parameters in CNC turning, influencing the efficiency and quality of the machining process.
1. Turning Speed (Spindle Speed):
Definition: Turning speed, often referred to as spindle speed, is the rotational speed of the lathe spindle and workpiece, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
Calculation: The turning speed is calculated using the formula:
Optimizing Manufacturing Processes with CNC Turning
Factors Influencing Speed:
Material: Different materials have different recommended cutting speeds.
Tool Material: Carbide tools can withstand higher speeds than high-speed steel tools.
Cutting Operation: Roughing operations typically require lower speeds than finishing operations.
2. Feed Rate:
Definition: Feed rate is the rate at which the cutting tool advances along the workpiece, measured in millimeters per revolution (mm/rev) or millimeters per minute (mm/min).
Calculation: The feed rate is calculated using the formula: Feed Rate (mm/min)=Cutting Speed (m/min)×Number of Inserts×Chip Load per Insert (mm)
Feed Rate (mm/min)=Cutting Speed (m/min)×Number of Inserts×Chip Load per Insert (mm).
Factors Influencing Feed Rate:
Material: Harder materials often require lower feed rates.
Tool Geometry: Different tools may have different recommended feed rates.
Depth of Cut: Deeper cuts may require lower feed rates to avoid excessive tool wear.
=
Cutting Speed (m/min)
�
×
Diameter (m)
Considerations:
Balancing Speed and Feed: Optimal cutting conditions balance speed and feed for efficient material removal without compromising tool life.
Chip Formation: Proper feed rates help in the formation of manageable chips, preventing chip evacuation issues.
Tool Life: High speeds and feeds can increase material removal rates but may also reduce tool life. Balancing these factors is crucial.
Surface Finish: Lower feed rates in finishing operations can improve surface finish quality.
Here are some factors to consider for your CNC turning project:
What is the number of parts needed in the long or short term?
(CNC turning centres are often well suited for prototyping and short-term production.)
What are the part sizes?
(The cost of turning a part depends on the quantity.)
Conclusion
CNC turning stands as a reliable and versatile manufacturing process, harmonizing cost-effectiveness with high-quality results. Precision-turned parts achieved through CNC turning provide a competitive edge in the marketplace. For unparalleled CNC machining services, GD-HUB emerges as the ideal manufacturing partner, offering tailored solutions to meet diverse project requirements.
Reach out to GD-HUB today for a collaborative approach to machining excellence.
https://www.gd-hub.com/cnc-machining/cnc-turning.html
Thread: CNC Turning Feedrate
Results 1 to 1 of 1
-
11-13-2023, 07:29 AM #1
 Member
Member
- Join Date
- Oct 2023
- Posts
- 5
 CNC Turning Feedrate
CNC Turning Feedrate





 Reply With Quote
Reply With Quote